In the first part of this practical guide on wood finishes (you can access it through this link), I analyzed natural products to protect it such as wax, shellac and oil. Now it is the turn of synthetic products, specifically polyurethane, varnish and lacquer.
Although at first it may seem that polyurethane, varnish and lacquer are the same product, this is not the case, each of them has its own properties and peculiarities as you will see below.
Wood finishes: polyurethane
Polyurethane is a resin with plastic base that provides a thick and resistant finish. You can find water-based and solvent-based polyurethane, as well as matte, satin and gloss finishes. It is one of the varnishes with better adherence to the surface and that more it is usually used in interior carpentry since it is appropriate for woods that must resist constant friction.
water-based polyurethane It has the advantage that its smell is barely noticeable, it is colorless and dries quite quickly, however it does not withstand heat or chemical products well, so its use is only recommended for interior furniture and that will not have very intensive use.

For its application, it is advisable to use synthetic bristle brushes since, as happens with water-based paints, natural bristles soften with an aqueous base (you can see my recommendations for painting with a brush or roller at this link). It can also be applied with foam and flocked (peach skin) rollers. In addition, for a perfect finish, it is advisable to sand between layers with very fine grit sandpaper (300 or more).
On the other hand, oil-based or solvent-based polyurethane it is more resistant to heat, shock and scratches compared to water-based. It is the one that is usually used for wooden floors or platforms, tables and countertops.
Synthetic polyurethane adds a slight yellowish color to the wood which can enrich your natural look and tone up dyes. It also has an intense smell, so it is best to work with it in a room that is well ventilated. For its application, it is recommended to use a natural bristle brush or a wool or multi-surface roller, although as in the case of water-based polyurethane, sanding between coats will be the key to a perfect finish.
Finally, it must be taken into account that when you want to protect a wooden piece of furniture with a stripped effect, both water-based polyurethane and oil-based polyurethane can be applied indistinctly over paints of both bases, although oil-based polyurethane will provide an amber tone, more accentuated in the case of light-colored paints.

In particular, I have used matte polyurethane on a stained wood bookcase and on a desk decorated with decoupage, obtaining a resistant finish in both cases.
Wood finishes: varnish
In the same way that it happens with polyurethane, varnishes can be classified into water-based and synthetic varnishesand you can also choose between a matte, satin and gloss finish.
The varnish is a solution of oils or resinous substances in a solvent, which evaporates in contact with the air, leaving a protective layer on the surface to which it has been applied. There are varnishes of natural origin (resins and essential oils from plants) and varnishes made with synthetic resins.
The acrylic varnishes or water-based, they dry very quickly, although they require several coats to obtain a result as resistant as that of a synthetic varnish.

The synthetic varnishes They take about 5 hours to dry and you must wait 24 hours to apply a new layer, preferably with a brush or brush with natural bristles. Its main advantage is that it is very resistant, especially the Spar or marine varnish, which is perfect for furniture that is going to be outdoors and exposed to moisture, as well as for exterior doors. This type of varnish protects the wood from both moisture and ultraviolet rays.
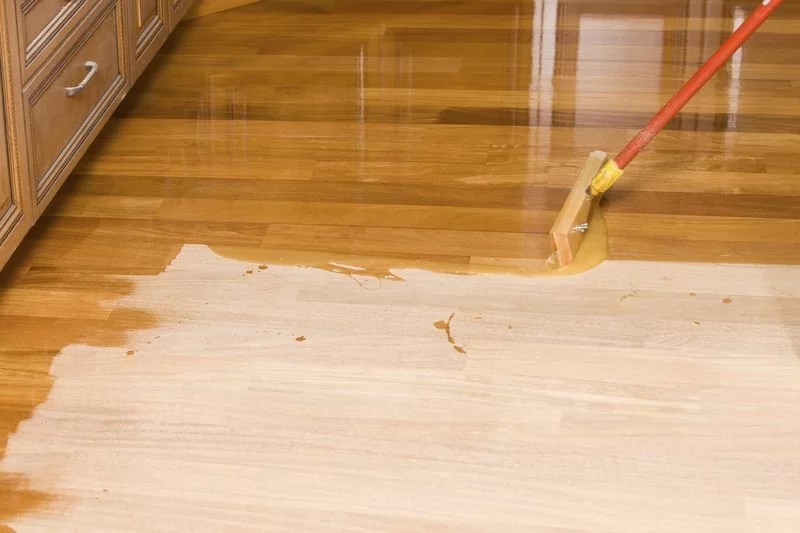

Regarding the finish, keep in mind that a glossy varnish will intensify the color of the wood but will also make its imperfections stand out. Satin varnish is the most widely used to protect floors, although it must be taken into account that it darkens over time. Lastly, matt varnish is quite resistant and is preferably used on doors and windows.
Wood finishes: lacquer
Lacquer gives the wood a glossy finish., smooth and durable, but like paint it hides its original grain. Although it can be used on any type of wood, the mdf boards (wood fiber agglomerate) are the most suitable for obtaining a smooth and homogeneous finish.
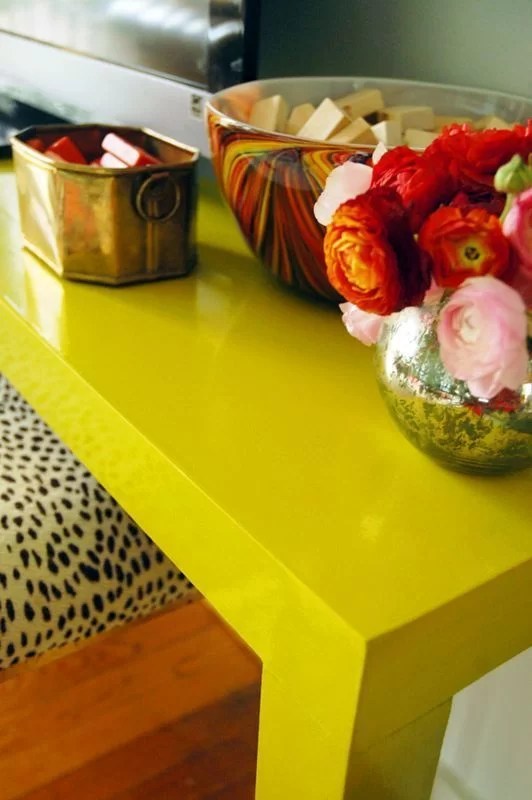

Image: Little Green Notebook
The main difference between lacquer and paint is that lacquer provides a crystal clear finish and is more durable than paint. In addition, its drying time is shorter and the color remains unchanged over time. As the main disadvantage, I would highlight that it takes some practice to get a good finish and avoid the most common problems associated with lacquering: lack of adherence and lumps or “orange peel”. It is also necessary to use a spray gun, since its texture is more viscous than that of other finishes.
Lacquer or lacquer finish is often used to protect modern or contemporary style interior furniture, although it can also be used to restore old furniture and give it a fresh look. On the other hand, it is possible to combine any lacquer color (RAL, NCS and Pantone charts) with wood to create personalized and highly decorative furniture.
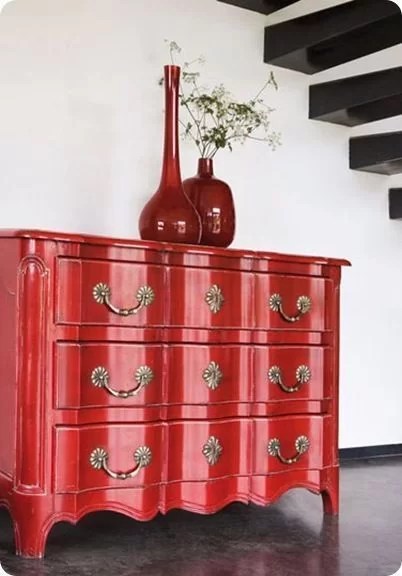

Image: Apartment Therapy
Summarizing…
The oil-based (or synthetic) version of polyurethane and varnish will always be more resistant than the water-based version, however, the latter dries much more quickly and does not add color to the wood.
polyurethane It has great adhesion and chemical resistance and is the most widely used in interior carpentryMeanwhile he varnish is more appropriate for woods that have to be outdoors such as doors and windows, since in addition to moisture it protects from ultra-violet rays.
On the other hand, the lacquer hides the grain of the wood and provides a very bright finish in keeping with a contemporary style. Its application must be carried out exclusively with a spray gun, so it requires some skill to achieve a good finish.
Finally the state of the furniture or object must be taken into account when applying any of these wood finishes. If the piece of furniture is already varnished, a test must first be carried out in a non-visible area of it to rule out any chemical incompatibility that could damage it. It will also be necessary to sand or strip to correct defects and homogenize the surface before applying a new layer of varnish.
With this second part of the guide on wood finishes the options of the first part are completed. Wax, oil, shellac, polyurethane, varnish and lacquer. Do you know which finish you are going to choose to protect your furniture and wooden objects?
If you liked this guide on the different finishes for wood visit , you will find many more practical guides and DIY projects.
[elfsight_youtube_gallery id=»1″]